Matchless Info About How To Increase Social Mobility

A comprehensive strategy to fight poverty and increase mobility would attack these causes on three fronts by aiming to increase the share of children growing.
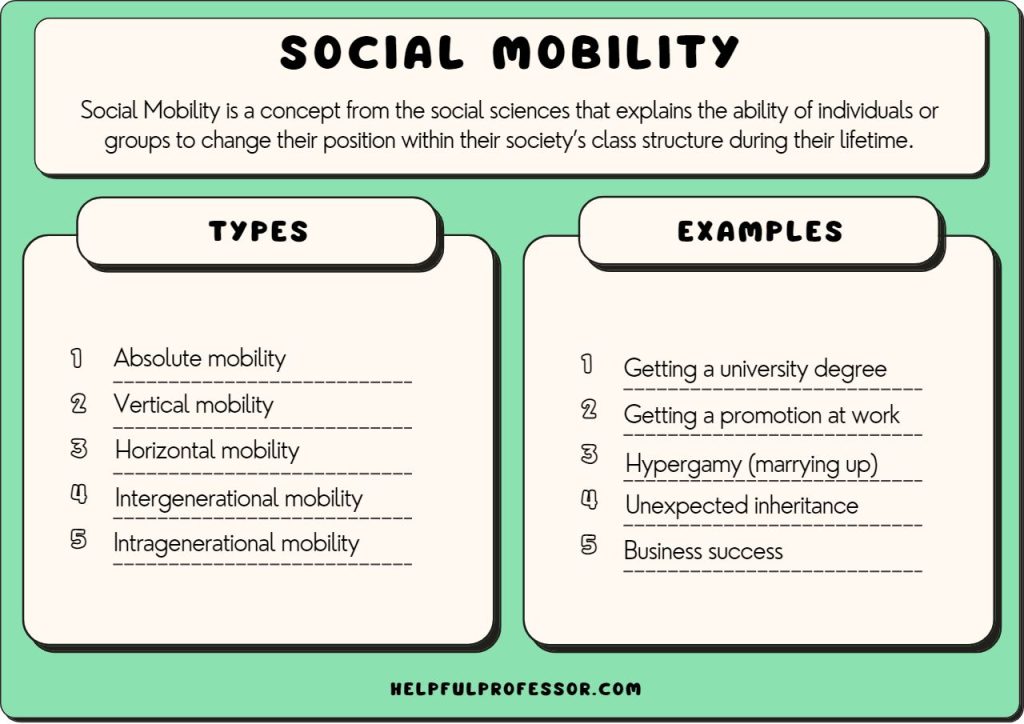
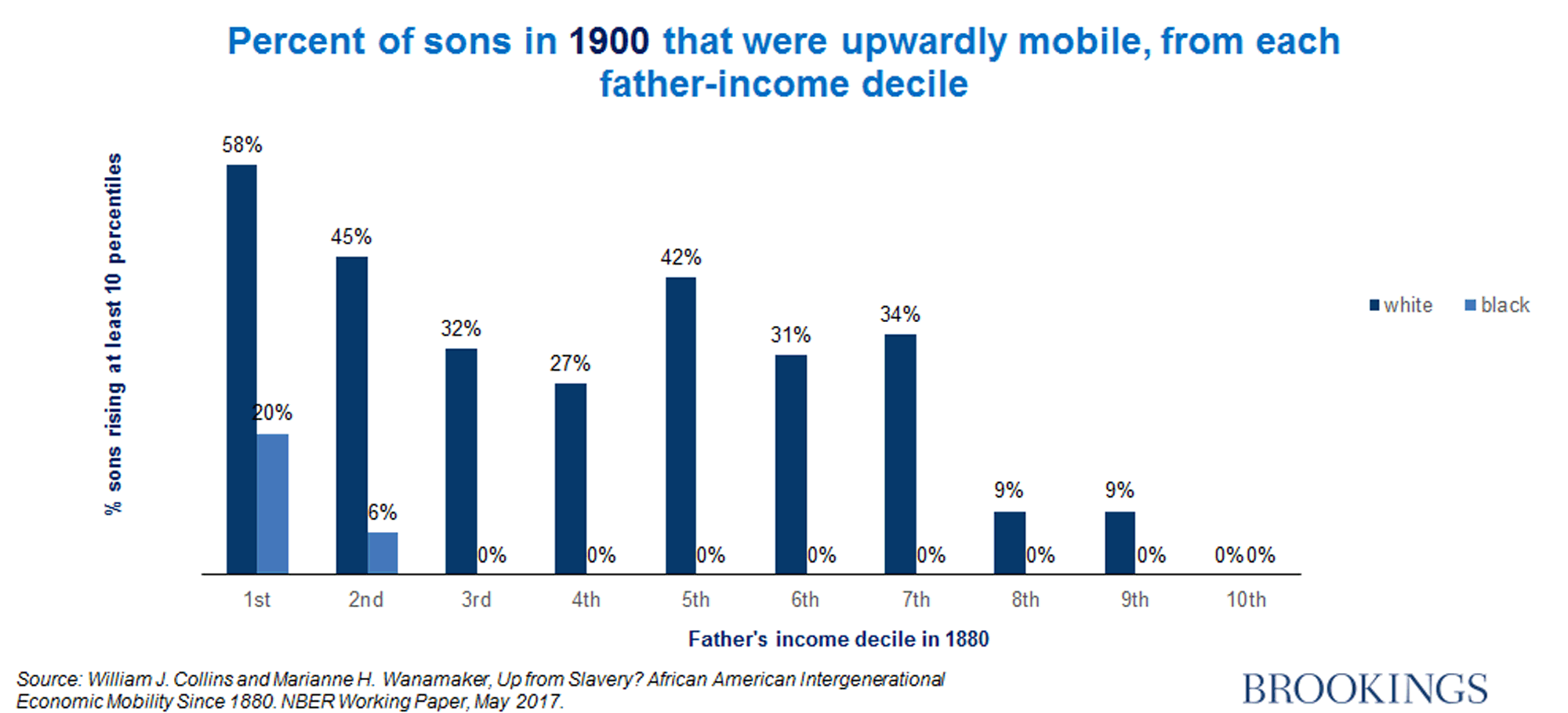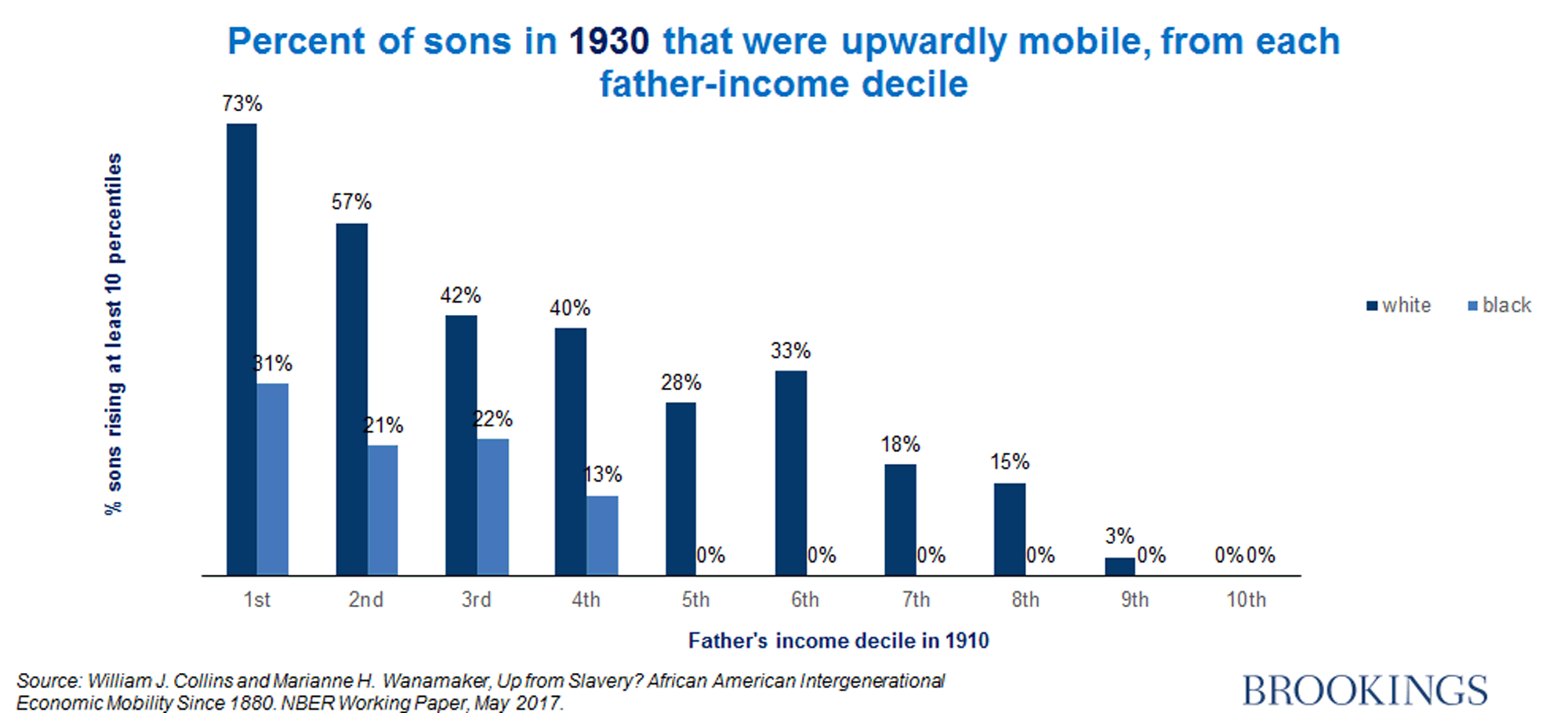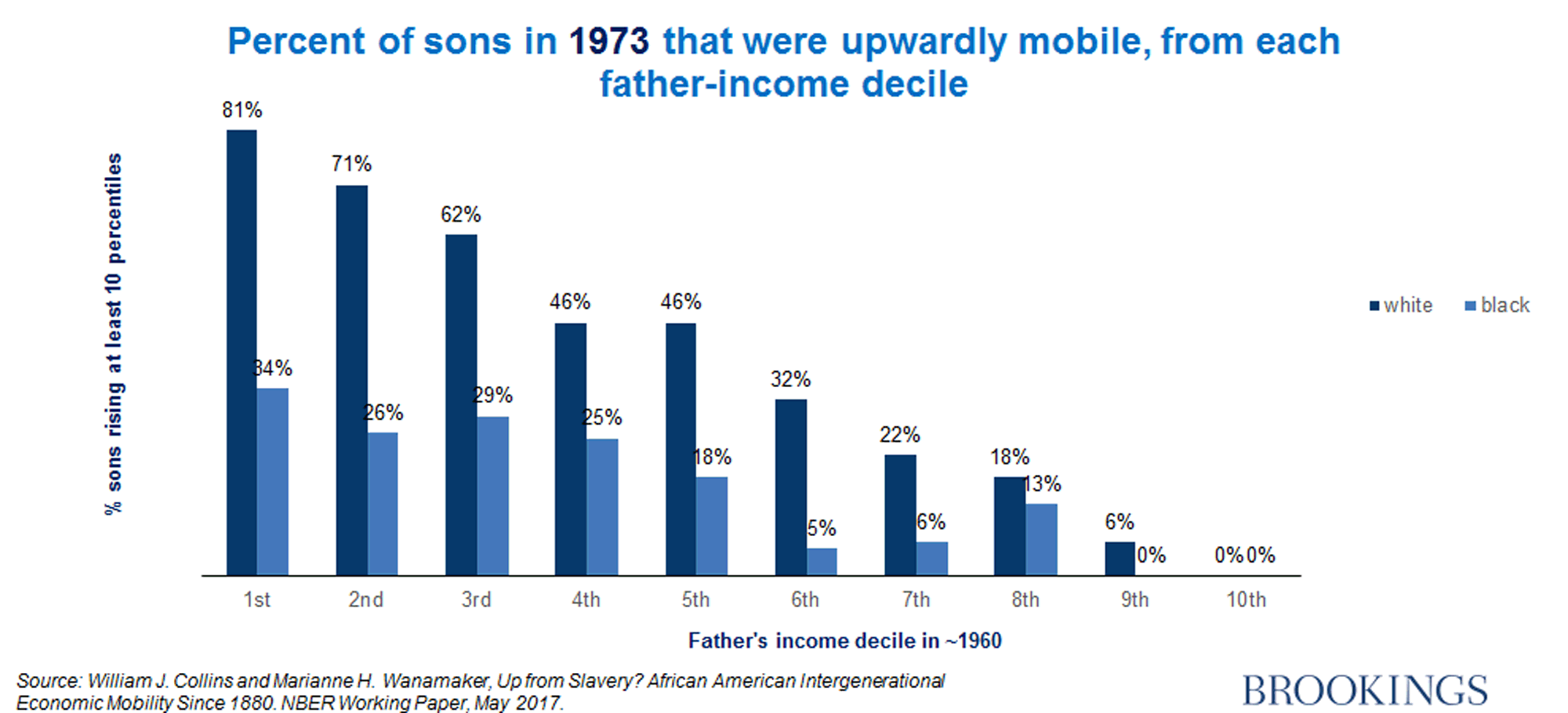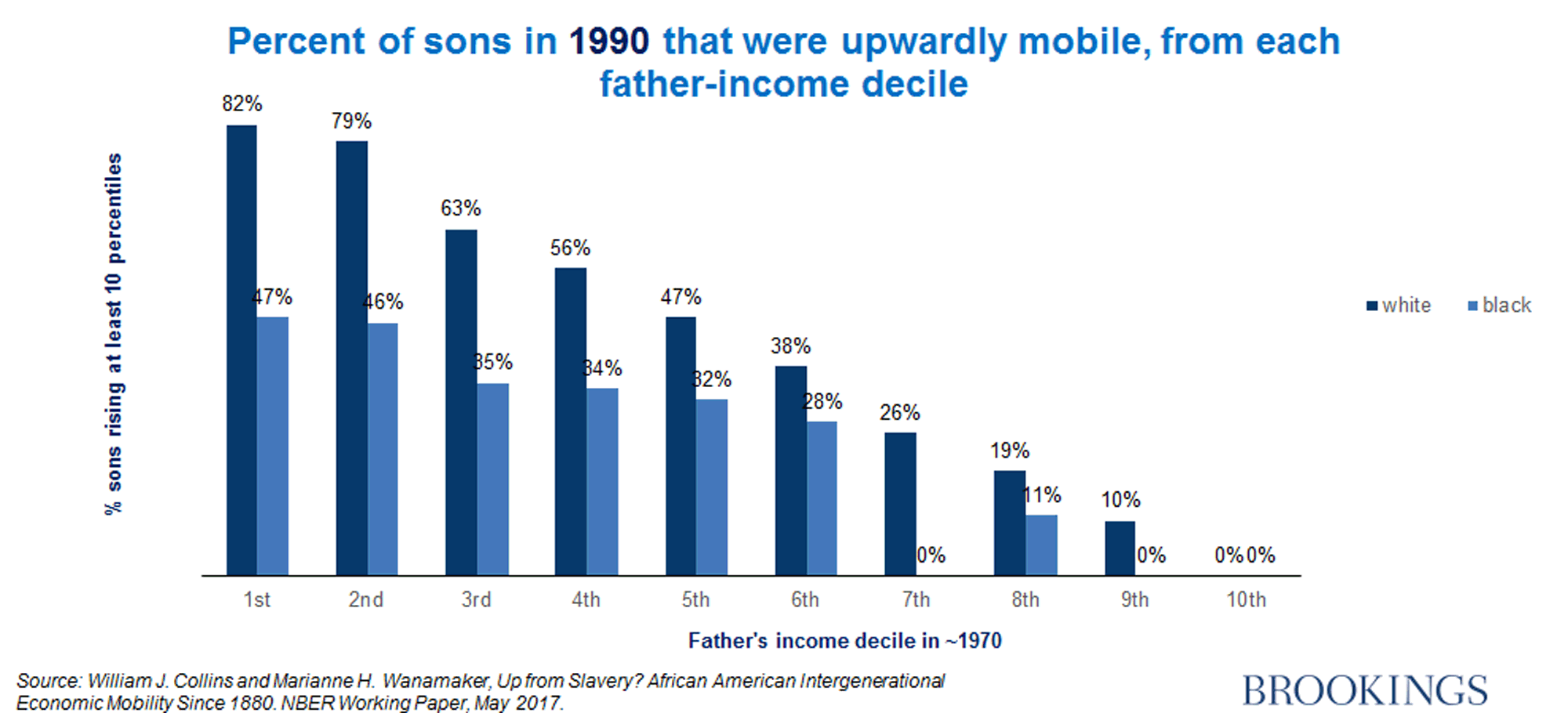
How to increase social mobility. The lack of social mobility has economic, societal and political consequences. Social mobility, movement of individuals, families, or groups through a system of social hierarchy or stratification. Data from the equality of opportunity project offer new information on how to improve social mobility in the united states.
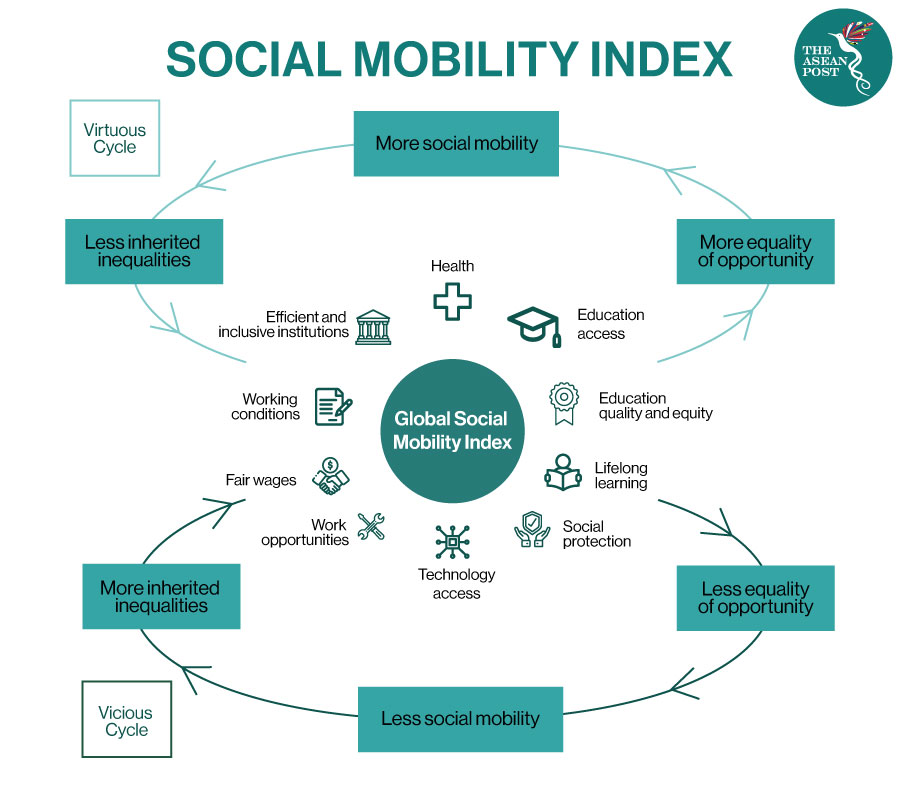
Health and family policies, education, labour market. In our book, social mobility and its enemies, we argued that the prospects for social mobility in britain are. Countries with high income inequality have low social mobility.
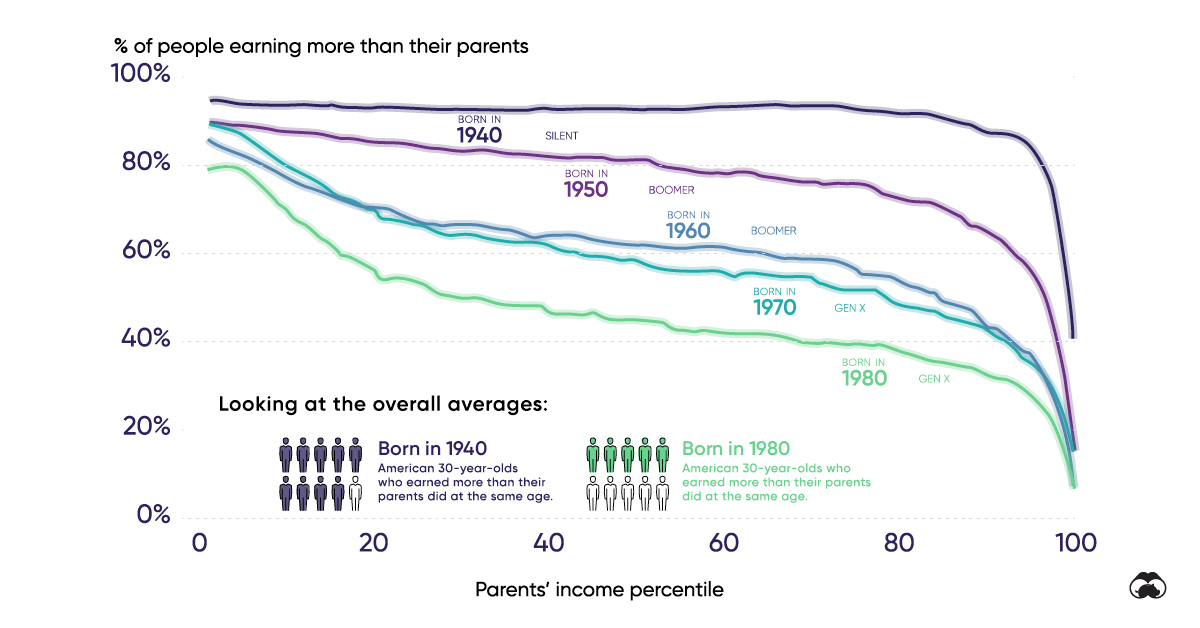
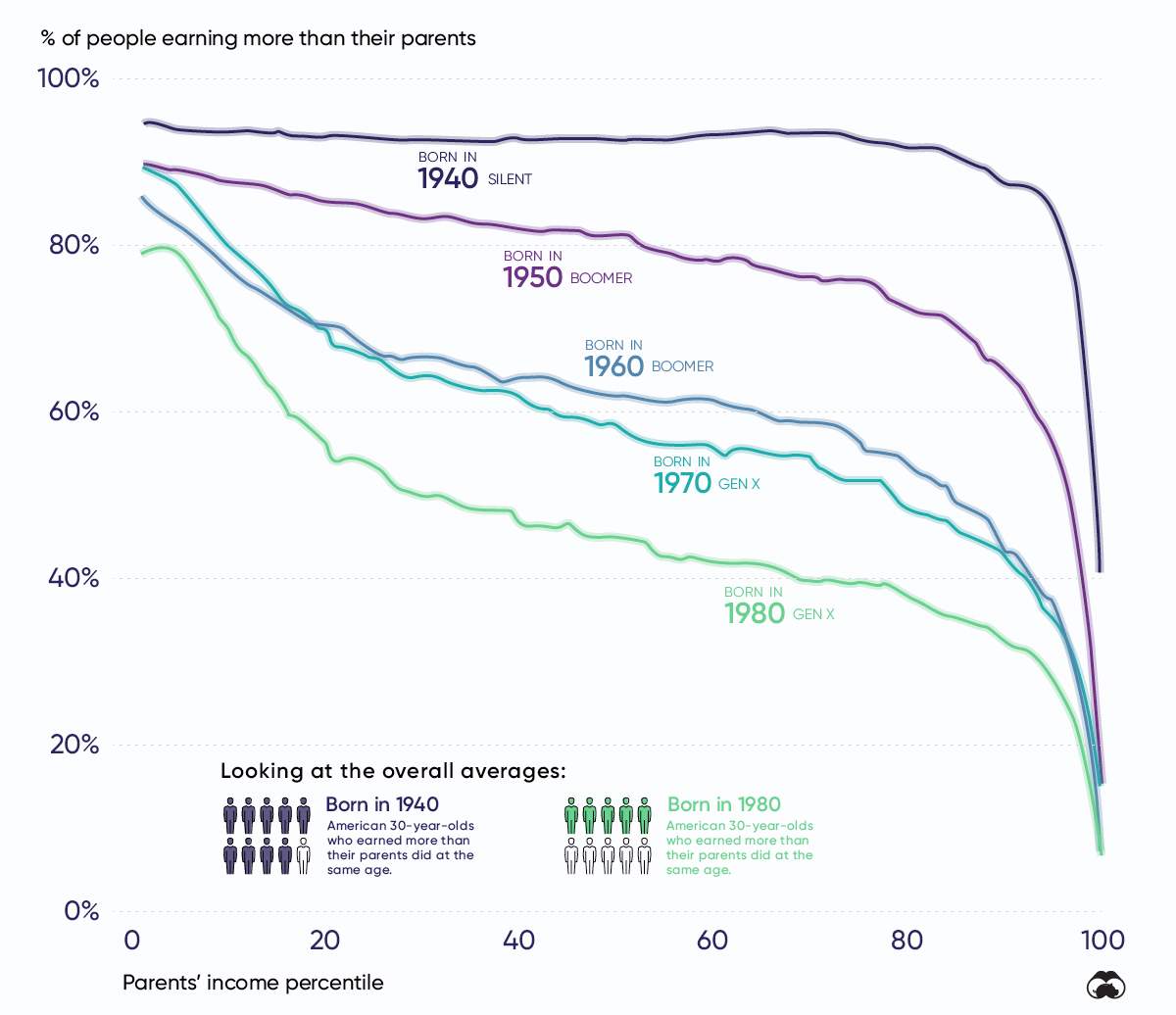
(11 pages) social mobility is a concept that considers people’s socioeconomic circumstances and the degree to which they change over a lifetime and. Family incomes have declined for a third of american children over the past few decades. The chapter identifies five broad policy areas on which countries should focus to improve citizen’s mobility prospects:
The social mobility commission monitors progress towards improving social mobility in the uk, and promotes social mobility in england. Add a resistance band or cable, away from the traveling leg, to increase difficulty. They’re related in that we might think.
The national plan for dealing with social mobility through education. Strengthening the lower body is important for a number of reasons: This report shows that there is space for policies to make societies more mobile and protect.
Politicians don’t want to hear the truth, which is that for people to climb the social ladder,. Social mobility is a dynamic concept referring to how people move throughout the income or wealth distribution, whereas inequality is more a static statement about, currently, how does the top 10 percent of the wealth distribution compare to the bottom 10 percent? In revolution an entire class structure is.
Social networks importantly influence individuals’ mobility prospects, both in tangible ways—via access to opportunities, information about jobs, referrals, etc.